Litecoin is a proof-of-work cryptocurrency designed with a little change to the code of Bitcoin. It first came into existence in October 7, 2011 and is currently the 10th largest cryptocurrency by market cap.
Table of Contents
History
Litecoin was a modification to the code of Fairbrix which was developed by Charlie Lee, an ex-computer scientist from Google and a MIT graduate. Fairbrix was itself developed from Tenebrix.
Tenebrix was one of the early altcoins which was made with the motive of designing a cryptocurrency with an endless supply. However, it was criticized because the founders wanted to keep 7.7 million Tenebrix tokens for themselves. Tenebrix had an unlimited token supply.
Charlie Lee modified Fairbrix code to create a cryptocurrency (then called as a peer-to-peer money) that has a limited supply of 84 million coins. It came out on GitHub on October 7, 2011, nearly 2 years after Bitcoin. The network went live 6 days later on October 13, 2011.
There are three other board of directors (beside Lee) at the Litecoin Foundation: Xinxi Wang, Alan Austin and Zing Yang.
How Does Litecoin Work
Litecoin works on a proof-of-work algorithm similar to Bitcoin where miners (who verify transaction) will have to solve a complex mathematical problem to arrive at values that help them sign blocks(list) of transactions.
This is different than proof-of-stake where only those who stake or deposit a certain amount are allowed to sign transactions.
Below is a flowchart which shows the working of Proof-of-Work blockchain such as Bitcoin, Dogecoin and Litecoin.
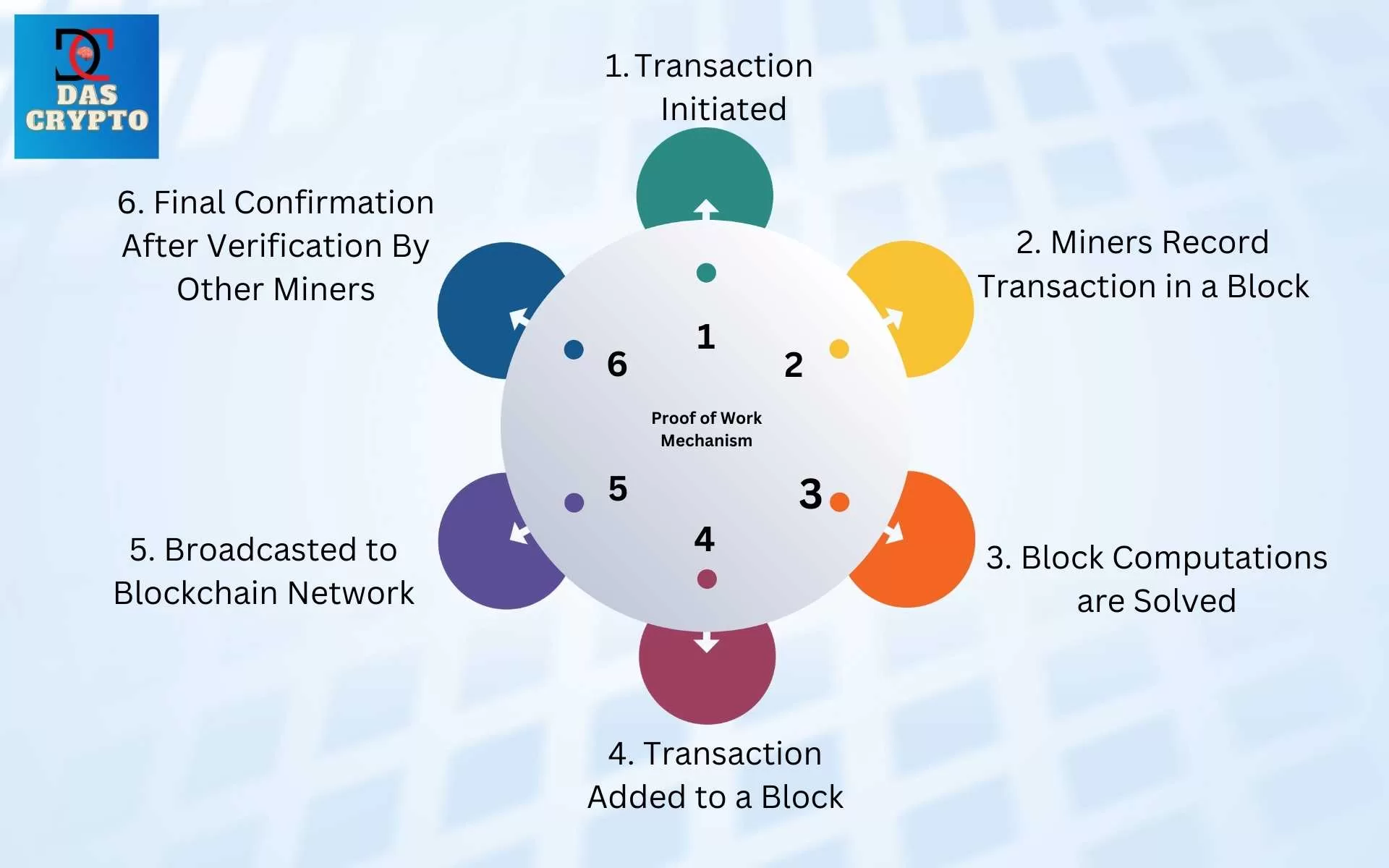
Litecoin was made to provide faster and cheaper transactions than the Bitcoin network, though after the Lightning Network, Bitcoin has become way much faster.
Technical Details
Block Time
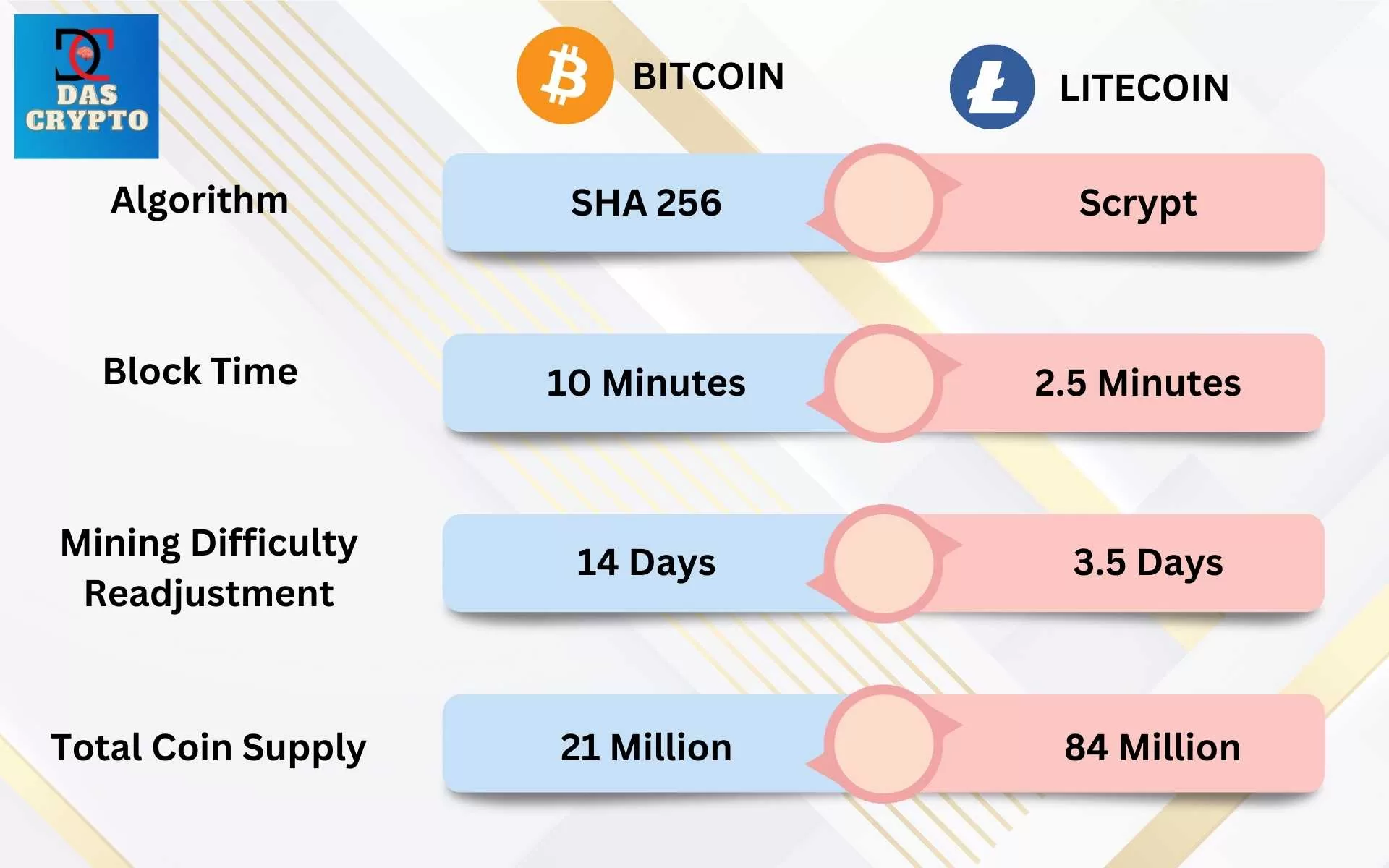
Litecoin has a block time of 2 min 39 seconds.
A block time is the speed at which new blocks are created. This is also the same time which is taken by a cryptocurrency transaction to finalize as this can only happen when the block which has those transactions are added permanently to a blockchain.
Proof-of-Work Algorithm: Scrypt and Merge Mining
Litecoin uses Scrypt, an alternate proof-of-work algorithm. Litecoin is merge mined with Dogecoin which means a miner can mine both coins using the same algorithm. Mining one cryptocurrency also helps secure the other. Also miners can potentially earn rewards from both cryptocurrencies by mining just one of them.
Mining Difficulty
Mining difficulty is the blockchain’s response to release controlled rewards in case more mining power is used. Litecoin having a faster block production rate has faster frequencies of difficulty adjustments.
The current frequency is every 3.5 days.
Block Explorer
Litecoin transactions can be verified using the following blockchain explorers:
- Blockchair https://blockchair.com/litecoin
- Chainz Crypto ID https://chainz.cryptoid.info/ltc/
- Litecoin Explorer http://explorer.litecoin.net/chain/Litecoin
- BSC Scan https://bscscan.com/token/0x4338665cbb7b2485a8855a139b75d5e34ab0db94
Differences From Bitcoin
Tokenomics
Litecoin has a total of 84 Million tokens out of which 73,345,252 coins are in circulation as per CoinMarketCap data on July 12, 2023.
Each Litecoin can be divided into 1000 Lites, or 1 million Microlitecoin or 100 million Litoshi.