The International Monetary Fund and The Financial Stability board has finally submitted a paper on crypto as requested by the G20, whose Summit takes place in India in 2023. The paper outlines the benefits as well as risks that crypto possesses to global economy.
The IMF and FSB Paper’s recommendations on crypto assets said that an outright ban on crypto assets would not be possible. However, it still sees them as risk for global economy.

Table of Contents
1. Risks Associated with Crypto Assets, as per the Report
The paper submitted by IMF and FSB outline many risks such as monetary risk, fiscal risk and exchange rate risk.
Monetary Policy Risks
The IMF and FSB paper outrightly says that a widespread adoption of crypto assets would risk global economy. They could undermine the effectiveness of monetary policy. They could also undermine the flow of capital, magnify financial risks and divert resources available for financing the economy.
- What is a Monetary Policy? A monetary policy is a strategy which controls the supply of currency in an economy. The policy is generally crafted and implemented by various central banks in their jurisdictions like the Federal Reserve in the USA, RBI in India, Bank of England in the UK, and others.
Fiscal Risks
The IMF and FSB paper advocates that there are ample financial risks for economies due to crypto. This is because a bulk of crypto payments have a cross-border nature which makes compliance possible only through a voluntary disclosure.
All of the above, according to the report, could impact the price stability of goods and services across the world.
Das Crypto’s Response
This would not have been a greater case if CBDCs were include basic features of blockchain technology like faster transactions and cheaper cross-border payments.
Still, crypto is not much of an asset to impact world financials or even a single country. There has been no countries where crypto has caused financial instability while there have been a lot of countries where IMF policies have caused widespread unrests and financial meltdown.
Exchange Rate Risk
According to the IMF and FSB paper, granting legal tender status or even official status to crypto would be a significant risk to the country’s economy and government’s tax collection. Low transactions in official currency would reduce its value and ultimately undermine the exchange rate.
Further, crypto assets could also prompt easy conversion and transfer of funds to abroad or safe tax havens. It is one of the reasons why China initially put a ban on crypto.
This risk is considerable because if crypto assets, which are mostly untraceable, would encourage people not to pay taxes and only show a small portion of their income as taxable income.
What is an Exchange Rate? An exchange rate is the rate at which a currency is exchangeable with other currencies. Each currency pair like the USD to GBP or INR to JPY have their own exchange rates. These rates are generally floating in nature and change constantly.
Das Crypto’s Response
Though this argument is valid for smaller and fragile economies, target ones like India, USA, China or the EU would not see much impact on crypto volumes on their monetary policies if they trace and address them at the right time.
At least CBDCs could implement basic blockchain technologies following the lead of PayPal’s PYUSD stablecoin and JP Morgan.
Environmental Risk
The report highlights that crypto assets that work on proof of work blockchains consume a lot of energy.
Das Crypto’s Response
Bitcoin, which account for the most of the market share in Proof of Work blockchains have been using much less energy than banks. It uses 56 times lesser energy than all of the banks, as per an article on Cointelegraph.
Further, more and more cryptocurrencies are moving towards proof of stake which consumes less than 0.01% of energy as compare to proof of work.
3. Threat to Emerging Economies
Crypto assets, as per the IMF and FSB paper, are threat to emerging economies where the incentives to use them are high. The following are the reasons submitted by the paper.
- Firstly, emerging and developing economies have a high inflation rate and more volatile currencies. This prevents people from using money as a store of value.
- Secondly, emerging economies have a lower per capital bank accounts. The lack of diverse set of investment actions, that take place via bank accounts are generally not available in such areas. This incentivizes the investment in crypto.
- Thirdly, due to the low rates of financial education, people in emerging markets are generally not aware of the risks in crypto.
- Fourth, Cross Border Payments are generally higher in emerging markets.
Das Crypto’s Response
There appears to be no practical correlation between inflation and crypto. Turkey, which was witnessing record inflation in Q4, 2022 had witnessed decreased amount of crypto purchases.
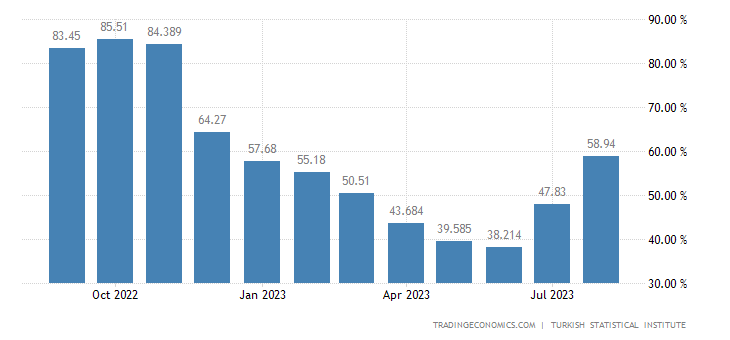
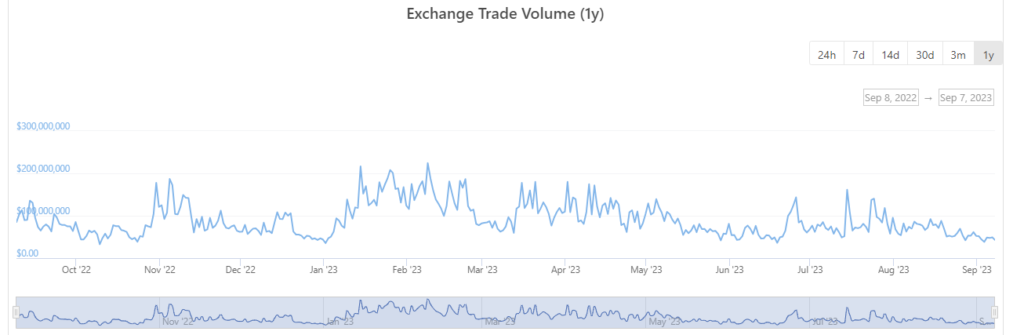
For the crypto trading data, we relied on Coin Gecko’s report on Paribu Exchange. Which accounts for 50% of crypto transactions in the country. We can see that in October 2022, when there was record inflation, the crypto trading volumes sank.
In fact, it was the months when there was low inflation, there was a record buying of crypto. See the months of June 2023 in the inflation data when it was 38% and it corresponds to a spike in crypto purchases on Paribu.
4. Recommendations of IMF and FSB Against Crypto
The IMF and FSB paper on crypto assets posts several recommendations on taxation, regulation, data collection, against official usage of stablecoins amongst others.
Avoid Blanket Bans
The IMF and FSB report recommends that blanket bans may be inefficient in handling crypto assets because of their difficulty to implement. Such bans are technically demanding due to the anonymous nature of blockchain addresses.
Even if temporary bans are necessary, they should be reciprocated with more wider and comprehensive regulations.
Strong Guard Against Flow of Capital to Crypto
The IMF and FSB paper also recommended that an unanimous approach to global crypto regulation, where the flow of money into crypto assets should be highly regulated. It also recommended that governments across the world keep a tight vigil in their realms and on their monetary policies. All of these will serve to restrict the flow of capital to crypto assets.
The paper also highlighted that crypto assets could also easily divert much needed foreign exchange that could be locally invested.
Taxation
Both FSB and IMF recommend that there should be a uniform set of taxes on cryptocurrencies so that no economy would allow itself to be used a crypto tax haven.
Tax authorities should leverage information from sources like exchanges, broker-dealers, and other sources.
Regulations
One of the key recommendations of the IMF and FSB paper were that crypto assets should not be granted legal or official status. Such a status would undermine the official currency. Further, crypto assets do not, reportedly, fulfil the status of a currency which is unit of account, means of exchange and store of value.
FSB recommends that authorities should investigate the connections between crypto and the wider financial system to address risks properly.
Collaboration on Cross-Border Information Sharing
Wider level of crypto asset ecosystem restricts the effectiveness of individual national regulations.
The IMF and FSB paper recommended that there should be a good framework like the Crypto Assets Reporting Framework that is currently being used by the OECD, to share information. This would increase institutional capacity. Further, there should also be specialized tax personnel for crypto assets.
Official Usage of Crypto
The IMF and FSB paper advises against the usage of crypto as official money as it may erode the power of central banks and governments over their control on monetary policy, discussed above in Sec 1 of this article.
Further, crypto assets increase the under-reporting of income which leads to erosion of tax base.
Also Read: Full Document of the IMF-FSB Synthesis Paper